

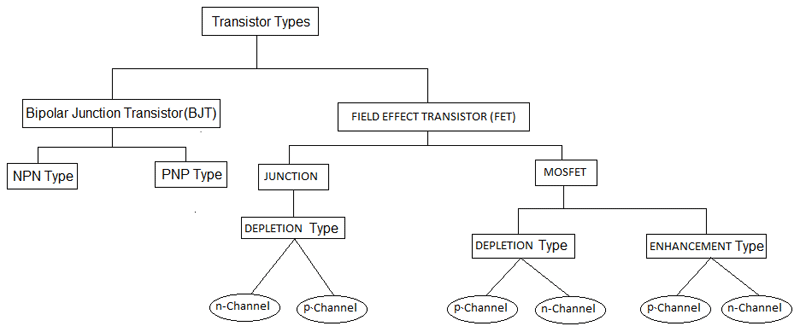
Bipolar junction transistors come in two major types, NPN and PNP. Bipolar Junction transistors are current-controlled devices. For p-n-p connection, the conservative current flows into the emitter as exposed by the inward arrow.Ħ Different Types of Transistors and Their Functionsīipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) BJT transistors which are built up of 3 regions, the base, the collector, and the emitter. This means that conservative current flows out of the emitter as an indicated by the outgoing arrow. In the n-p-n connection we identify electrons flow into the emitter. Transistor Symbol The arrow symbol defined the emitter current. A transistor is a device that regulates current or voltage flow and acts as a button or gate for electronic signals.Ĥ Different Types of Transistors and Their Functionsĥ Different Types of Transistors and Their Functions A transistor is the combination of two diodes it is a connected back to back. When a semiconductor is placed in centre between same type semiconductors the arrangement is called transistors. It is made through p and n type semiconductor. What is Transistor The transistor is an electronic equipment. There are low, medium and high power transistors, for functioning with high and low frequencies, for functioning with very high current and or high voltages.ģ Different Types of Transistors and Their Functions They are used as amplifiers and switching apparatus. Introduction: Transistor is an active component and that is establishing in all over electronic circuits. Data Bits The bit width of the component's inputs and outputs.Presentation on theme: "Different Types of Transistors and Their Functions"- Presentation transcript:ġ Different Types of Transistors and Their FunctionsĢ Different Types of Transistors and Their Functions Gate Location The location of the gate input. Facing The direction of the component (its output relative to its input). Type Determines whether the transistor is P-type or N-type. When the component is selected or being added,Īlt-0 through Alt-9 alter its Data Bits attributeĪnd the arrow keys alter its Facing attribute. Or an error value, then the output will be an error value. Input is the negation of what indicates negation. If indicated by the gate input, or will be floating if the gate East edge (output, bit width matches Data Bits attribute) The component's output, which will match the source input This will trigger the transistor if the gate value is 1. Will transmit if the gate value is 0 for N-type transistors,
North edge (input, bit width 1) The component's gate input. Pins (assuming component faces east, gate line top/left) West edge (input, bit width matches Data Bits attribute) The component's source input that will transmit to the output Is that a transistor is meant for more basic circuit designs. If the Data Bits attribute is more than 1, the gate input is stillĪ single bit, but its value is applied simultaneously to each of theĪn N-type transistor behaves very similarly to aĬontrolled Buffer. * If source is Z, drain is Z otherwise drain is X. When gate is 0, while an N-type transistor (which has no such circle) (indicated by a circle on the gate line) transmits The determination of transmitting or disconnectingĭepends on the type of transistor: A P-type transistor The value at source may be transmitted toĭrain or there may be no connection from source, Plate, while the N-type transistor has no such circle. Transistor is indicated by a circle connecting the gate input to its Transistors, with slightly different behaviors described below the P-type The gate input is drawn connected to a plate that is parallel to the Logisim draws an arrowhead to indicate the direction of flow from input to output. Input and drain output are drawn connected by a plate A transistor has two inputs, called gate and source,Īnd one output, called drain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
